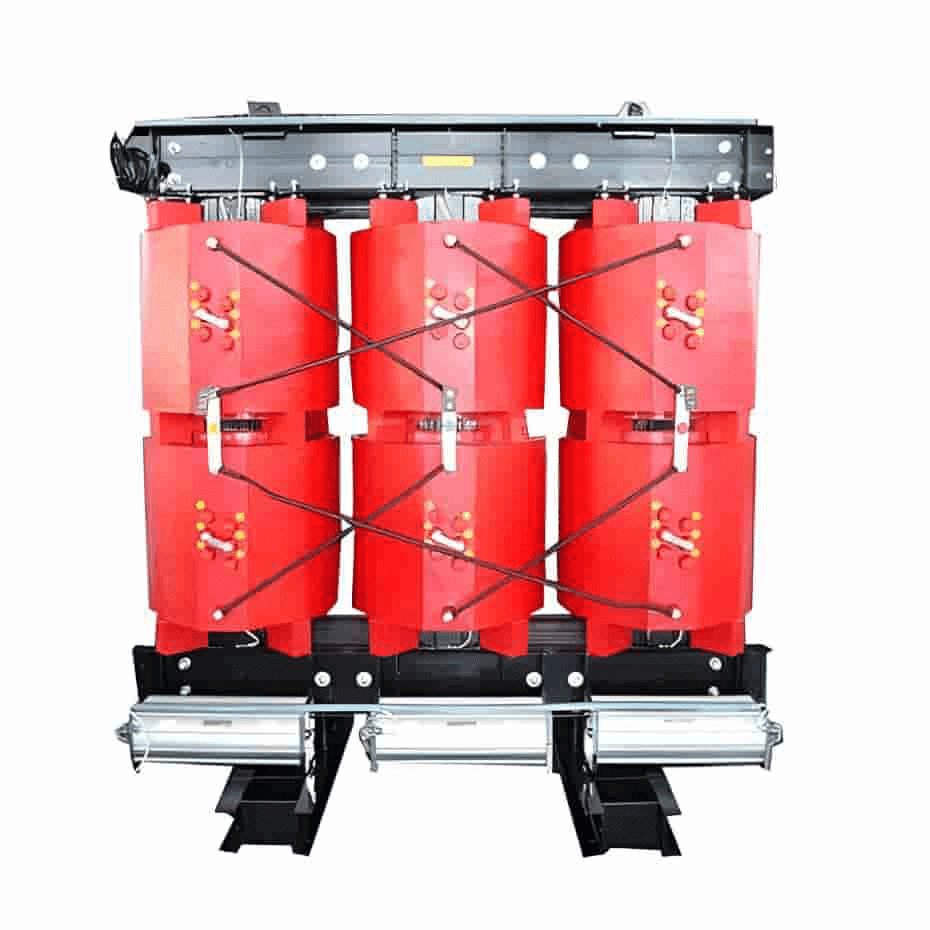
New Energy Split Transformer
1.Scope of application
New Energy Split-winding transformer refers to a multi-winding power transformer consisting of one high-voltage winding and two or more low-voltage windings with the same voltage and capacity in each phase. The normal power transmission of the split transformer is only carried out between the high-voltage and low-voltage windings, and it has the function of limiting the short-circuit current in the event of a fault; Mainly used in fields such as photovoltaic power generation system, energy storage system, and industrial power distribution
2. Product standards
GB/T1094.1 GB/T1094.11 GB/T1094.12 GB/T10228 JB/T10088
GB20052 GB/T7354 JB/T3837 GB/T4208 IEC60076-11
3. Operation environment
1) Altitude: ≤1000 meters.
2) Ambient temperature: Maximum +45oC, Minimum -30oC.
3) Relative humidity: ≤90% (+25 oC).
4) Max Ground ramp degree: ≤3°.
5) Seismic level: ≤0.3m/s2 at horizontal direction and ≤0.15m/s2 at vertical direction.
6) Installation environment: No obvious and heavy pollution, no explosive and corrosive gas and dust, with good air ventilation and no severe vibration and shock.
7) If the application environment is different from the above standard conditions, please contact for customized designs.
4. Product advantages
1) Safe flame retardant, fireproof, explosion-proof, pollution-free, can be directly installed in the load center.
2) Low loss, maintenance-free, low comprehensive operating cost, obvious energy-saving effect.
3) Good moisture-proof performance, can operate normally at 100% humidity, and can be put into operation without pre-drying after decommissioning.
4) Partial discharge capacity< 5Pc, low noise, strong heat dissipation ability.
5) Strong load capacity, low product temperature rise, strong heat dissipation capacity, 140% load when forced air cooling to meet temporary emergency needs
6) Foil coils are insulated with DMD prepreg cloth to improve short-circuit resistance and service life.
7) Limit short-circuit current: When a low-voltage branch short-circuits, the current must flow through the high-impedance path (semi-through impedance) between the high-voltage winding and the other low-voltage branch, thereby significantly reducing the short-circuit current amplitude and protecting the system equipment.
8) Improve system reliability: When a low-voltage winding fails, the voltage fluctuation of the other branch is minimal, which can maintain normal power supply and improve system reliability
9) Cost-effectiveness: The two low-voltage branches can be connected to different loads or inverters respectively, supporting independent operation or parallel expansion to meet the needs of multiple scenarios