The connection DYN11 refers to a specific configuration used primarily in three-phase power transformers. This configuration defines the winding connections and the phase shift between the primary and secondary windings of the transformer. Here's a breakdown of what DYN11 means:
D: This letter denotes the type of transformer connection on the primary (high voltage) side. In this case, "D" stands for Delta, meaning that the primary windings are connected in a delta configuration. A delta connection involves connecting the ends of three windings together to form a closed loop, with no neutral point available directly from this connection.
Y: The second letter indicates the connection type on the secondary (low voltage) side. "Y" signifies a Wye or Star connection, where one end of each of the three windings is connected to a common point called the neutral. This configuration allows for a single-phase supply with a neutral line and also facilitates the use of a ground connection at the neutral point.
N: The presence of "N" confirms that there is a neutral point available, which is a direct reference to the neutral in the Wye (Y) connected secondary side.
11: These two numbers denote the phase shift between the primary and secondary windings in terms of clock hours. Specifically, "11" means the secondary voltage lags the primary voltage by 330 degrees electrical angle, which is equivalent to saying the transformer has a 30-degree phase shift (since a full cycle is 360 degrees, and 360 - 330 = 30). This phase shift is inherent in most transformers due to the way they are designed and wired and is particularly relevant when considering power factor correction and vector group considerations in power systems.
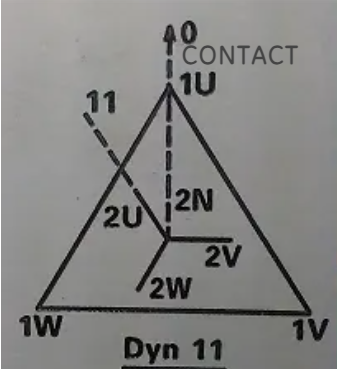
In summary, a DYN11 transformer connection implies that it has a Delta-connected primary winding and a Star-connected (with neutral) secondary winding, with the secondary voltage lagging the primary voltage by 30 degrees. This configuration is commonly used in distribution networks where a neutral is required for earthing purposes and for supplying single-phase loads, while still benefiting from a balanced three-phase system.